SEO Automation: What Is It and How Does It Work?

An interesting situation in SEO arises because of the people who tend to be most into it as an industry and a concept: SEO automation. We're generally tech-savvy people with an eye toward optimization, streamlining, and accelerating the things we do. I know I've either coded up (or signed up for) tools to make doing parts of my job more manageable, and I know I'm far from alone.
Many people working in SEO are always looking for ways to automate various processes and search engine optimization tasks we need to handle daily, weekly, and monthly. Some parts of SEO can be tedious, like link audits, content audits, outreach, editing, and competitive research.
Sometimes it's easy, like using a scraper to harvest data or scheduling tools to automate posting to social media. Other times it's more challenging, more complex, time-consuming, or even frowned upon by the authorities at Google, who determine what is acceptable for marketers to automate and what isn't.
So, what is SEO automation?
A lot goes into it, so let's break it down in this beginner's guide!
What Goes Into SEO Automation?
SEO, in general, is a combination of mechanical factors and human factors.
- The things that impact your SEO can be tangible, measurable, and mechanically-affectable qualities about your website. Site speed, for example, depends entirely on a combination of factors such as your web host, site code, infrastructure, and ensuring assets are delivered intelligently to visitors. It's as unbiased and impartial as a metric can be. Users can experience your site at vastly different speeds (compare someone accessing your mobile site on an LTE connection to someone accessing your desktop site on a high-speed fiber connection), and Google takes that into account. The SEO measurement comes from Google's servers and real-world lighthouse results from visitors on various mobile connections.
- On the flip side, you have on-page SEO and user-based metrics like the nebulous concept of the "user experience," qualities like bounce rate, and even link building. That's right; even link-building is a biased metric. You can't go out and build links yourself; every source of them you can make automatically is either spammy or devalued as user-generated content (like forums, blog comments, and social media posts.) Every good backlink you get comes from someone else deciding to add a link to your site, which is an inherently manual process.
To define SEO automation:
Yes, even link-building; I'll get to that in a bit.

Let's break down different elements of SEO and how you might be able to automate them, both in good and bad ways.
Finally, before we dig in, I want to make a distinction. Many people talk about automation as solely SEO automation software. My definition is a little broader. I include automation that you can do with tools and ways to automate more complex tasks through outsourcing. Remember, there are plenty of cases where something "automated" was just low-paid workers on the other end.
Here are seven SEO categories that you can potentially automate (either partially or entirely) to enhance your marketing efforts:
1. Technical Site Improvements
There are a lot of minor optimizations you can make to your site to improve your SEO, and many of them can be made automatically. For example:
- Internal linking. The proliferation of "related post" plugins is one example. Still, there are systems that will detect relevant keywords throughout your site and link to relevant posts you've published to ensure you have plenty of internal links. There's no such thing as "too many" internal links as long as those links are helpful to the user.
- Technical SEO factors. Things like page meta descriptions, image alt text, and other factors can all impact your SEO and can be created or optimized with automatic tools. Modern AI-based tools can generate image alt text based on image recognition (which is even part of ADA compliance!). You'll still want to do a manual overview to ensure it all works and is optimized, but you can do the bulk of the work with seo automation tools.
- Speed enhancements. You can automate many simple tasks like smushing down images when you upload them and generating multiple sizes for different viewports; you can minify scripts and CSS, and so on, all of which can be done automatically.
Automation in these sorts of improvements can save you a lot of time, though they aren't going to be perfect. You can always get better results by looking at each aspect of your site and doing it yourself. But, if you have a website with 5,000 web pages on it and 4,800 of them don't have image alt text, using an AI system to give you something for them will be a better improvement than plugging away at it 20-50 at a time and getting bored out of your mind. Plus, you can better spend that time doing other things.
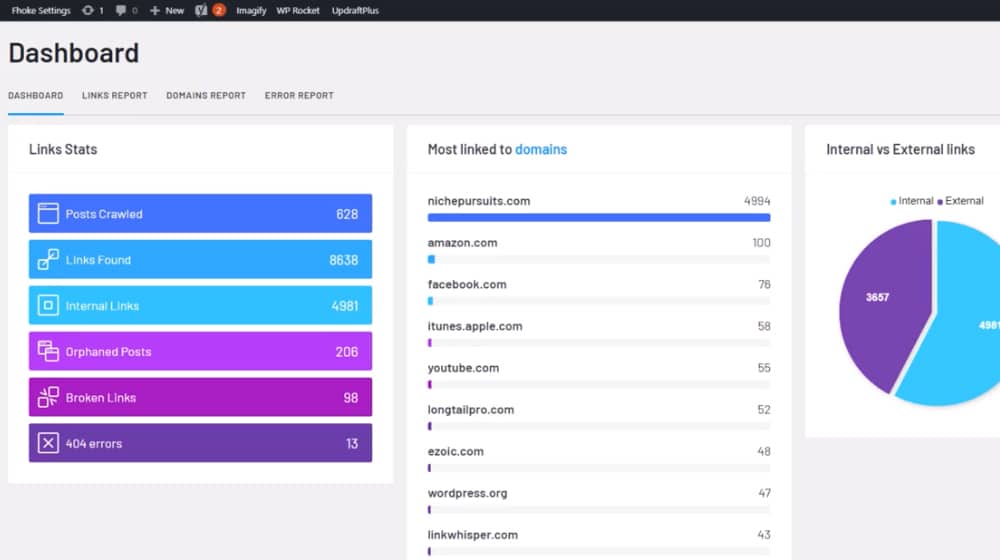
Side note, if your site needs a bunch of technical work in addition to content marketing, check out my services page. I'm more than happy to bring your site up to speed while working on your blog.
- PageSpeed automation: WP Rocket for WordPress, Nitropack for WordPress, and Hyperspeed for Shopify
- Accessibility compliance: AccessiBe
- Internal linking: Link Whisperer for WordPress and various alternatives
- Link checkers: Broken Link Checker for WordPress, Ahrefs, Screaming Frog
2. Site Monitoring and Auditing
Site monitoring can be pretty significant, as can auditing. These are usually technical reporting tasks, so it's relatively easy for an automated system to generate audit reports and keep an active monitor going.
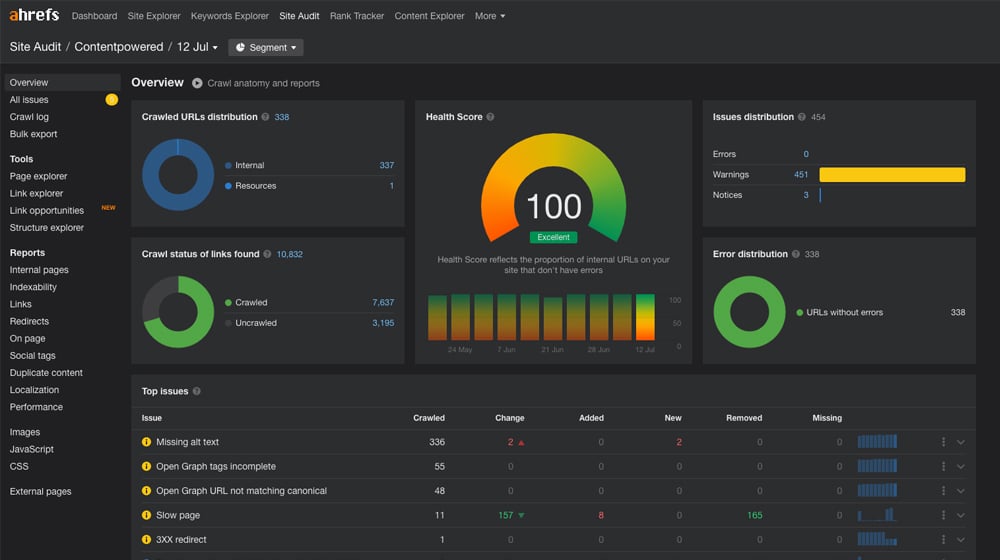
There are dozens of businesses offering SEO audits using automated auditing tools, and other options you can install that will generate internal audits instead. For example, you can use plugins to monitor your security and track spam attempts to brute force your login page or create logs of when files are edited. You can also run periodic (weekly, monthly, quarterly) website audits for various technical SEO elements.
- Site audit tools: Ahrefs and Semrush
- Security automation: WordFence for WordPress, Limit Login Attempts Reloaded
3. Analytics and Reporting
Much like monitoring and auditing, you can also automate general analytics and reporting. It's arguably one of the most-used forms of SEO automation. Generating reports is a risk-free technique (assuming you aren't using illegal means to obtain your data, of course). Reports, generated automatically, can be beneficial for making data-driven decisions.
Some things like Google Analytics are automatically generated in the background, but there are other kinds of SEO reports you can generate automatically as well.
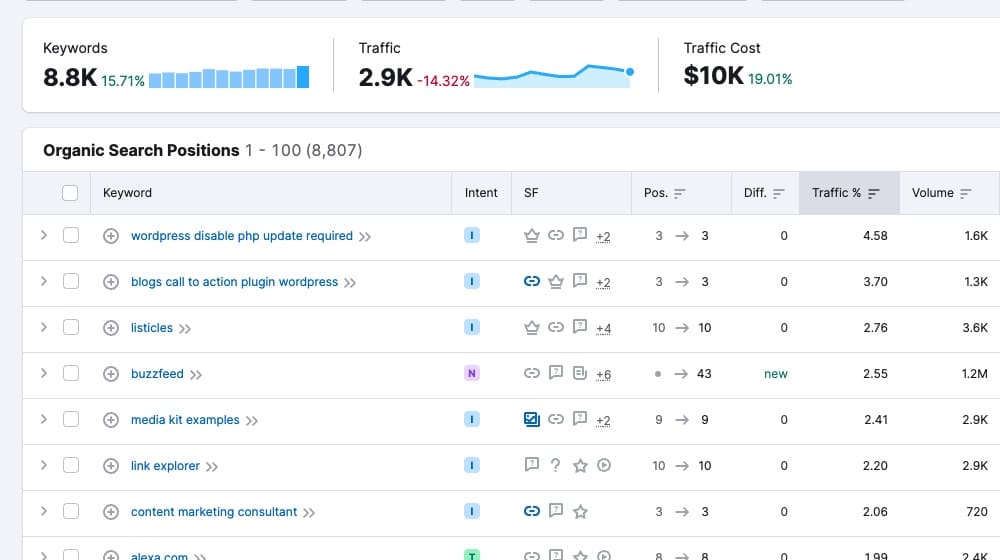
Automating analytics and report generation makes it easier to track how well your marketing efforts are working. These can be things like:
- Site rank tracking and SERP tracking per keyword, country, search engine, and page.
- Backlink analysis and tracking (pulling DA values, followed status, etc.)
- Competitor monitoring to see what your competition is doing at any given time.
- Brand mention monitoring to look at marketing effort success and link-building opportunities.
It takes a decent amount of front-loaded effort to decide what to monitor and how to present reports, but once you've created them, they run on a schedule and give you the information you need in your inbox or dashboard without further input.
Many of the best tools, like Semrush and Ahrefs, have automatic features to perform these kinds of research and report generation.
We create blog content that converts - not just for ourselves, but for our clients, too.
We pick blog topics like hedge funds pick stocks. Then, we create articles that are 10x better to earn the top spot.
Content marketing has two ingredients - content and marketing. We've earned our black belts in both.
- Analytics: Google Analytics, Google Search Console, Ahrefs, Semrush
- Backlink tracking: Ahrefs, Semrush, SE Ranking
- Competitor monitoring and brand mentions: Twitter, Google Trends
4. Split Testing and Ad Automation
This section is less for SEO and more for other, more direct marketing, but I'm still including it since it's all interconnected. Split testing is often used for landing pages, site design changes like button colors and positions, CTA testing, and ad offers testing. It can also include variations in blog post headlines, newsletter subject lines, etc.
Various testing and optimization platforms out there can generate variations and test them with your audience automatically, depending on the venue.
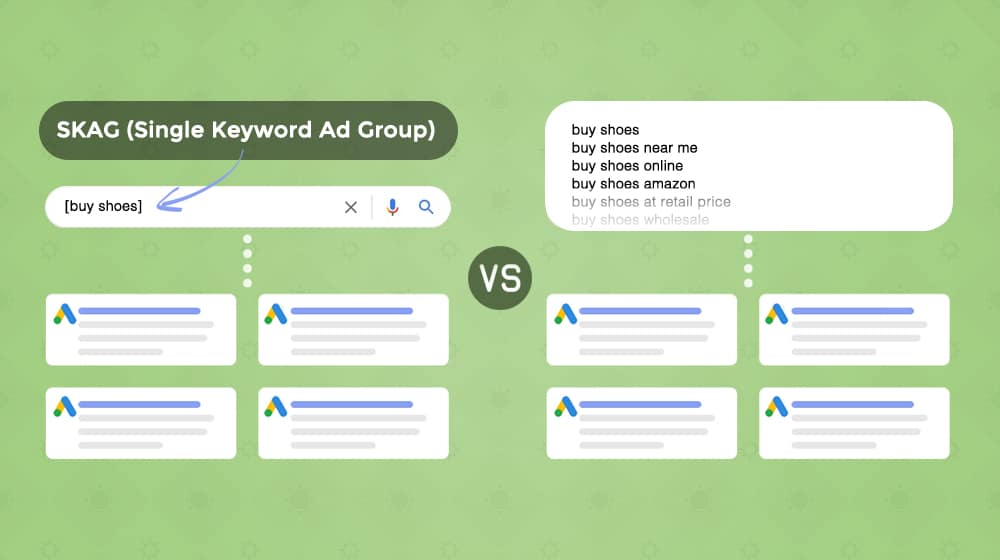
It's usually a feature built into other systems rather than a stand-alone automation tool.
Ad testing is similar. Various ad management platforms allow you to one-click generate variations on ads for testing (so you upload, say, two or three variations on ad copy, on an image, and the offer, and have it generate every possible combination with a click) which you can iterate on as you gather data to find which ones work best.
Again, PPC isn't SEO (they're two sides of the same coin), but better exposure through more effective PPC can also improve your SEO in various ways.
- Split testing: Hellobar, Nelio AB Testing for WordPress, Hotjar heat maps
- Backlink tracking: Ahrefs, Semrush
- Ad testing: Wordstream, AdEspresso
- Competitor monitoring and brand mentions: Twitter, Google Trends
5. Link Building
Automatic link building is where things start to get risky. As I see it, link building has two kinds of automation.
- The first is the worst. It's automated "outreach" and link submission. Things like automating generating blog comments with links back to your site, submitting your links to every possible directory under the sun, and building a list of the contact emails and forms for every single blogger in your industry - are bad news. All of this is considered spammy and will get you blocked, banned, and even removed from the search index if you're particularly egregious about it.
- The other kind of link-building automation is the good stuff, and it's what everyone in marketing should be doing (and probably are doing), even if they don't quite realize it. What is it? Publishing great tools, resources, and evergreen content (particularly link bait.)
Think about it:
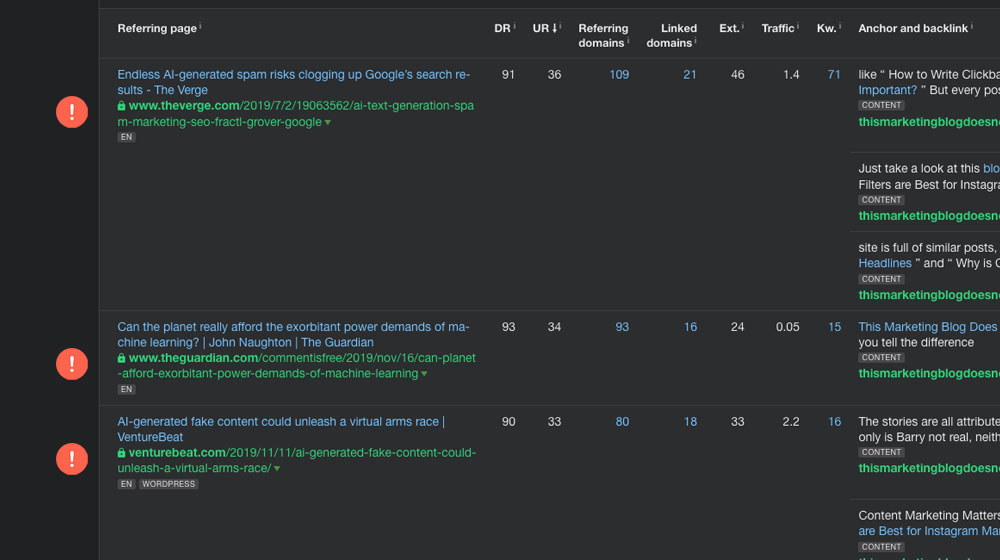
- A considerable resource post generates links passively for as long as it's relevant. For example, I've linked something like the Backlinko "search ranking factors" article dozens of times.
- A tool you create, like a free SEO audit tool or a headline analyzer, can generate links and traffic passively for years.
Creating these kinds of content should be the goal of most content marketers.
Passively building links, traffic, keyword rankings, and visibility is the end goal of pretty much everything we do.
- Blog content: Great evergreen blog content attracts links naturally over time, and you never have to think about it or build another link again. In the past month, I received links from massive sites like Hootsuite, Search Engine Journal, Wix, and many more. How much work did I do to receive those? Well, I just posted quality blog articles!
- Infographics: Infographics tend to pull in far more links than your average blog post, though they can take quite a bit more time and resources to data mine, design, and promote.
- Free Tools: People love free things and often link to them in blog posts. Create them, and links will appear organically! Some examples could include free calculators, checkers, testers, templates, calendars, and more.
6. Keyword Research
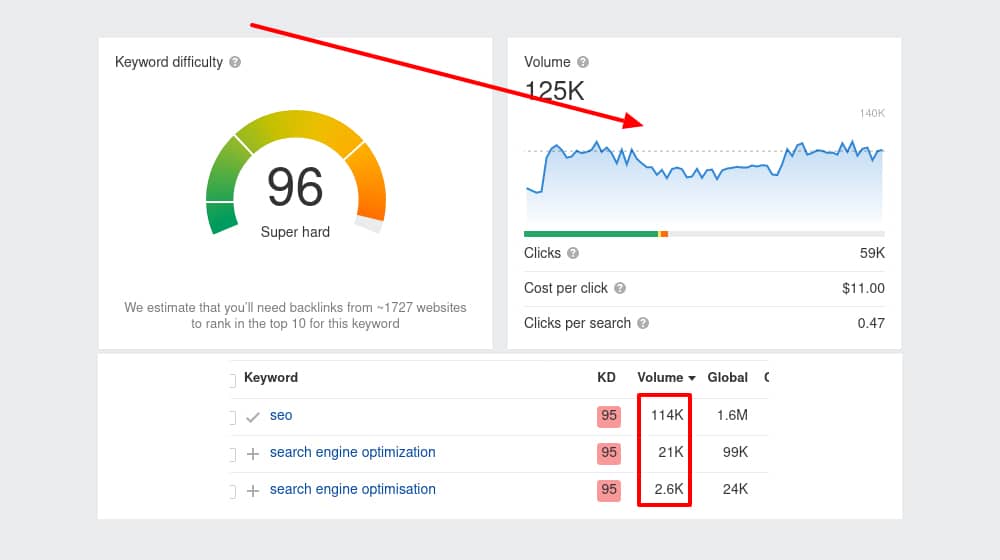
Keyword research is challenging to automate, but you can do the bulk of the work with a few automatic tools. For example, using tools to scrape all of Google's autocomplete suggestions and "people also asked" questions can give you a large document with potential keywords and topics relating to a given seed keyword.
The trouble is that while you can generate large lists of keywords this way, you don't have additional data to support which ones are better than others and which ones you should target. You need different systems for that, and since many keyword analysis tools charge by the keyword, it can be expensive to automate it in bulk.
The best way to fully "automate" keyword research is to outsource it to a consultant. Contract someone, an SEO agency or a freelance SEO expert, to do a bunch of keyword research for you and present a vetted report of the best opportunities available. Trust me; you don't want to skimp on the topic research process.
- Keyword volume: Google Keyword Tool, UberSuggest
- Organic traffic estimates: Ahrefs, Semrush
- Topic brainstorming: Twitter, Reddit, RSS readers, Google Questions Hub
7. Content Creation
The core of modern SEO is content creation and marketing, so how can you automate content creation?
Once again, there are two ways: a good way and a wrong way.
The wrong way is, unfortunately, growing more popular. It's the AI writing tools you see pushed pretty heavily. While these tools can help you with outlining and idea generation, the idea that you can use them to pump out content with the click of a button isn't going to work. Maybe in 5-10 years, but not right now.
Similarly, article spinning takes existing content and swaps out words to make something "original" for you to publish. It's pretty transparent and uncomplicated for Google to detect, though, so it doesn't work either.
The easiest way to automate content creation is to pay for it in bulk from content mills. That barely works, either, since the content you get from the mills will be low quality and unfocused and won't work together because different people are making it.
- Grammar checking: Grammarly
- Images: Stock photo sites, Canva
- Uniqueness checking: Copyscape
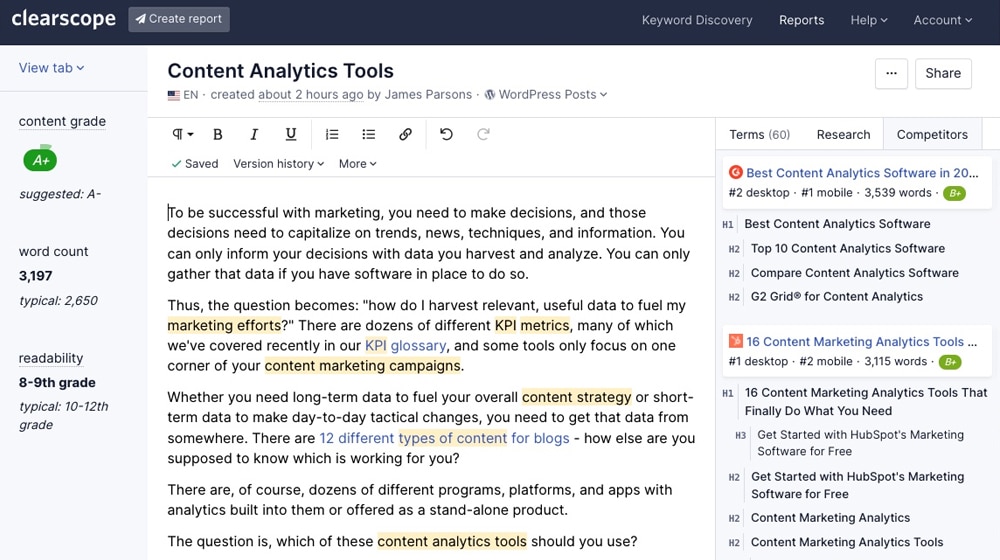
- Content analysis: Clearscope, Marketmuse
Actual content creation is a whole process that you can't truly automate. Like with keyword research, the best way to "automate" content creation is to pay an agency like mine to do the process for you. You get the dedicated human touch and the analysis, planning, and focus you need for your digital marketing and SEO efforts to succeed.
It's more expensive than paying for credits with an artificial intelligence tool or buying content for $15 a blog post from a content mill, but it's the closest you'll get.






Comments